Agile Culture
What is an Agile Culture?
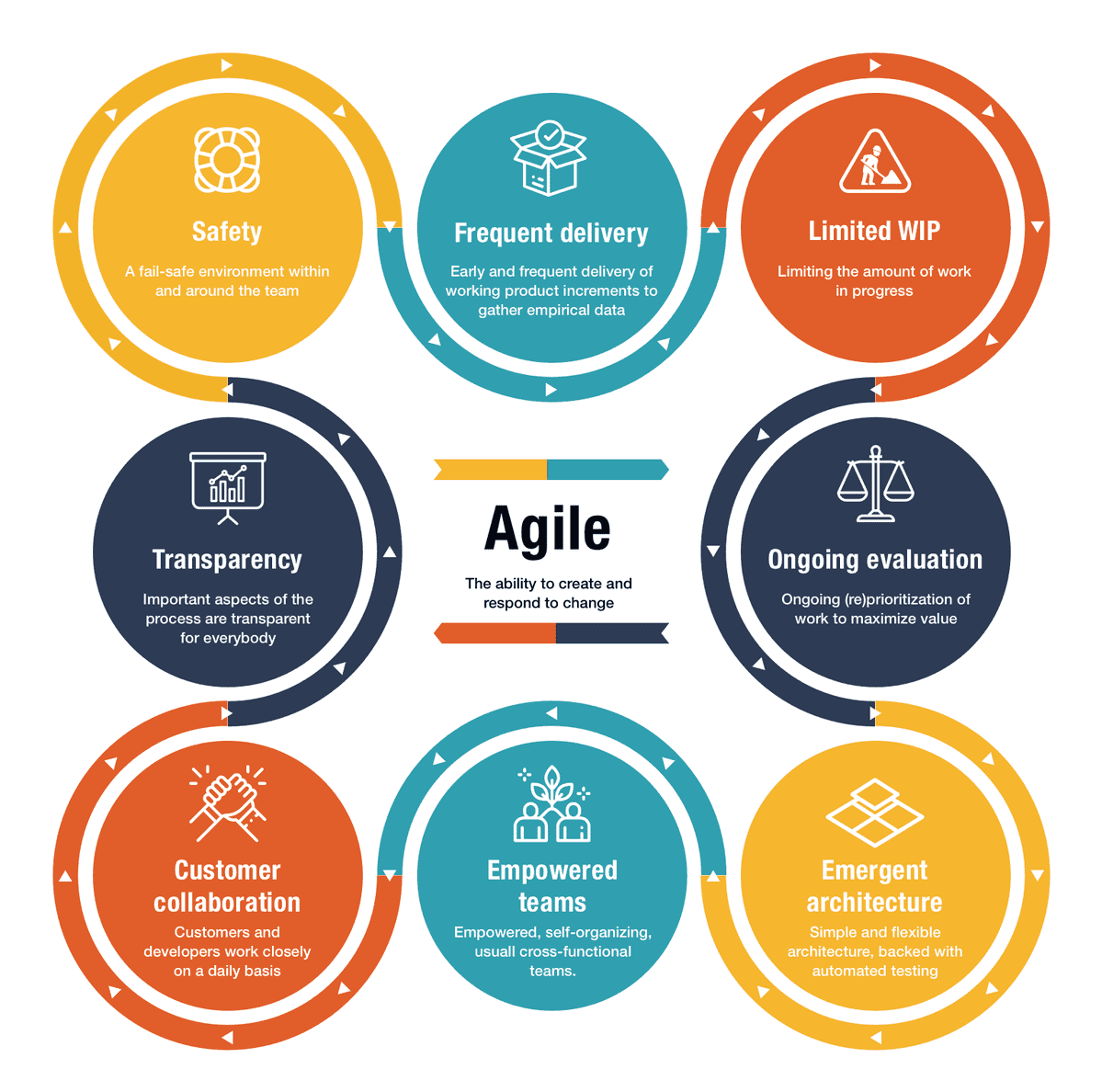
Definition:
An “Agile Culture” within the realms of project management and organizational behavior refers to an environment that embraces the principles and values of Agile methodologies. It involves fostering a mindset of adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement across teams and throughout the entire organization.
Analogy:
Imagine an organization as a dynamic ecosystem. An Agile Culture is akin to creating a fertile soil where innovative ideas can thrive, and teams can adapt to change seamlessly. While not dictating every move, it sets the conditions for teams to grow, collaborate, and deliver value iteratively.
Further Description:
Companies striving for an Agile Culture aim to instill agile principles in their DNA. This involves promoting open communication, transparency, and a focus on delivering customer value. An Agile Culture encourages experimentation, learning from failures, and a shared responsibility for continuous improvement at all levels of the organization.
Why is an Agile Culture Important?
An Agile Culture is crucial for organizations navigating the complexities of the modern business landscape. It promotes a mindset of adaptability, allowing teams to respond quickly to changes in customer needs and market dynamics. This culture fosters collaboration, innovation, and a sense of shared purpose, ultimately contributing to sustained success.
Examples and Usage:
Open Communication: Establishing channels for transparent and open communication within and across teams.
Iterative Improvement: Encouraging teams to regularly reflect on their processes, identify areas for improvement, and experiment with new approaches.
Customer-Centric Approach: Shifting the focus from internal processes to delivering value to customers and responding to their evolving needs.
Adaptability: Embracing change and empowering teams to pivot quickly in response to market shifts or feedback.
Basically, Agile culture aims to create an organizational mindset that values adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement. However, the implementation may vary depending on the industry.
For example, while Agile culture may involve implementing Scrum ceremonies and emphasizing customer collaboration for a software development business, it may focus on Kanban principles and lean thinking for a manufacturing organization.
Key Takeaways:
- Agile Culture embraces the principles and values of Agile methodologies across teams and the organization.
- It fosters adaptability, collaboration, and continuous improvement, promoting a customer-centric mindset.
- An Agile Culture encourages experimentation, open communication, and shared responsibility for success.
- It is crucial for organizations navigating the complexities of the modern business landscape.




