Founder’s Equity
What is Founders Equity?
Definition:
“Founders Equity” refers to the ownership stake or shares held by the founders of a company. It represents the portion of the business that founders have in terms of ownership, often expressed as a percentage. Founders equity is a crucial component of a startup’s capital structure and is typically earned through the contributions, efforts, and risks taken by the founders in the early stages of the company’s formation.
Analogy:
Think of Founders Equity as shares in a family-owned business. Similar to family members holding ownership stakes in a business they founded, founders equity represents the ownership held by the individuals who initiated and established a company.
Further Description:
Allocation of Ownership:
Founders equity is allocated among the individuals who played a foundational role in creating the company. This allocation is determined based on various factors, including the founders’ roles, responsibilities, and contributions.
Vesting Periods:
Founders’ equity may be subject to vesting periods, during which founders earn their equity over time. Vesting ensures that founders remain committed to the company and its long-term success.
Protecting Founder Interests:
Founders often use legal agreements, such as shareholders’ agreements, to define the terms of equity ownership, rights, and responsibilities. These agreements help protect the interests of founders and ensure a clear understanding of their roles within the company.
Why is Founders Equity Important?
Alignment of Interests:
Founders equity aligns the interests of the founders with the success of the company. As owners, founders are motivated to work towards the growth and profitability of the business.
Attracting Talent:
Founders often use equity as a tool to attract and retain key talent. Offering equity stakes can be a powerful incentive for employees and key team members to contribute to the company’s success.
Fundraising and Valuation:
The distribution of founders’ equity is a crucial consideration when seeking external funding. It influences the company’s valuation and attractiveness to potential investors.
Examples and Usage:
Co-Founder Agreements:
Co-founders typically outline the distribution of founders’ equity in a formal co-founder agreement. This agreement defines each founder’s ownership stake, responsibilities, and the terms of equity vesting.
Investor Negotiations:
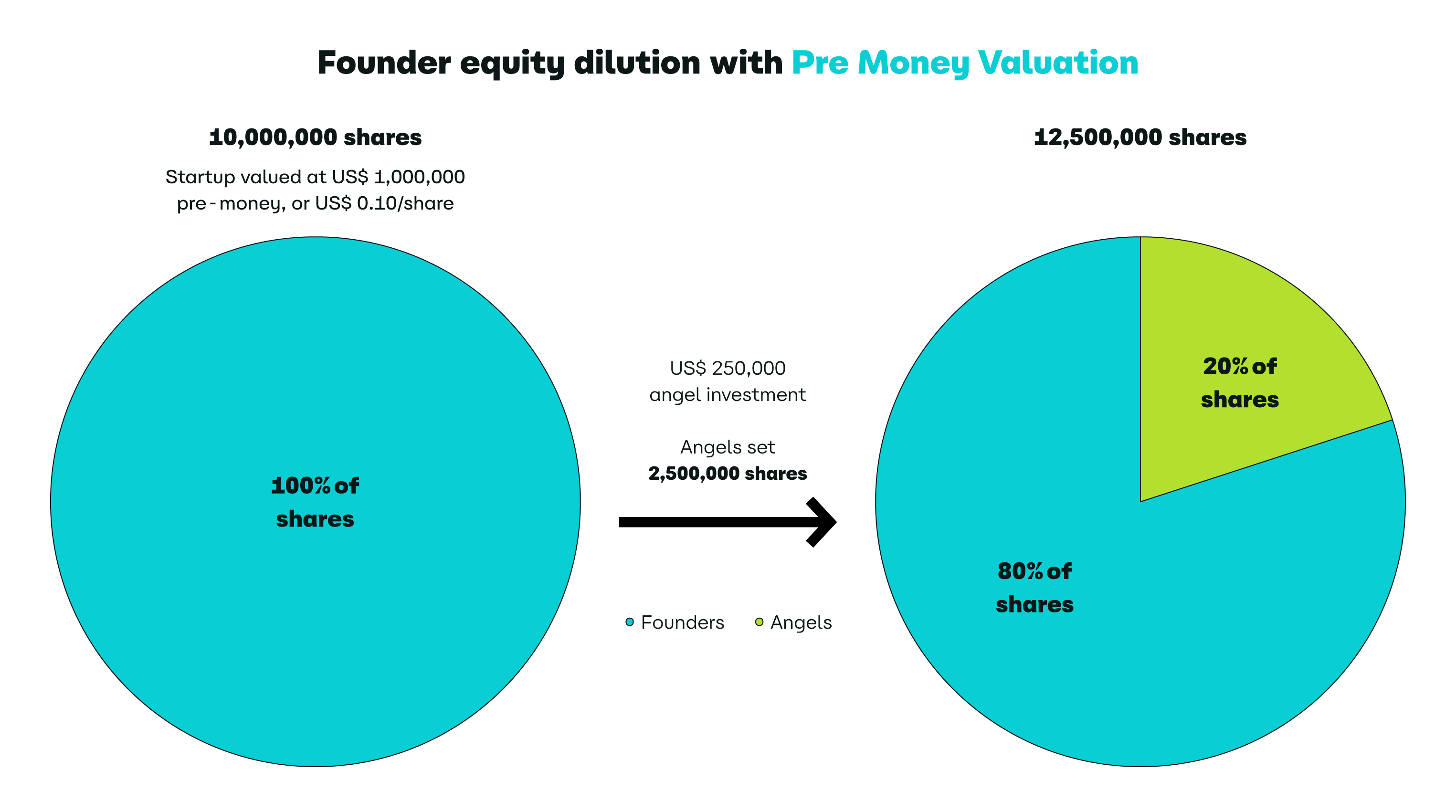
When negotiating with investors, founders may need to consider the impact of equity dilution. Dilution occurs when new investors are issued shares, reducing the proportional ownership of existing shareholders, including founders.
Exit Strategies:
Founders’ equity plays a significant role in exit strategies, such as mergers, acquisitions, or initial public offerings (IPOs). Understanding the distribution of equity is crucial during negotiations for such events.
In summary, Founders Equity represents the ownership stake held by the founders of a company. It is a vital aspect of a startup’s structure, influencing motivation, talent acquisition, fundraising, and long-term success.
Key Takeaways:
- Founders Equity is the ownership stake held by the founders of a company, often expressed as a percentage of the total equity.
- It aligns the interests of founders with the success of the business and serves as a motivational tool.
- Founders use legal agreements to define equity distribution, protect interests, and outline terms of ownership.