Hosting
What is Hosting?
Definition:
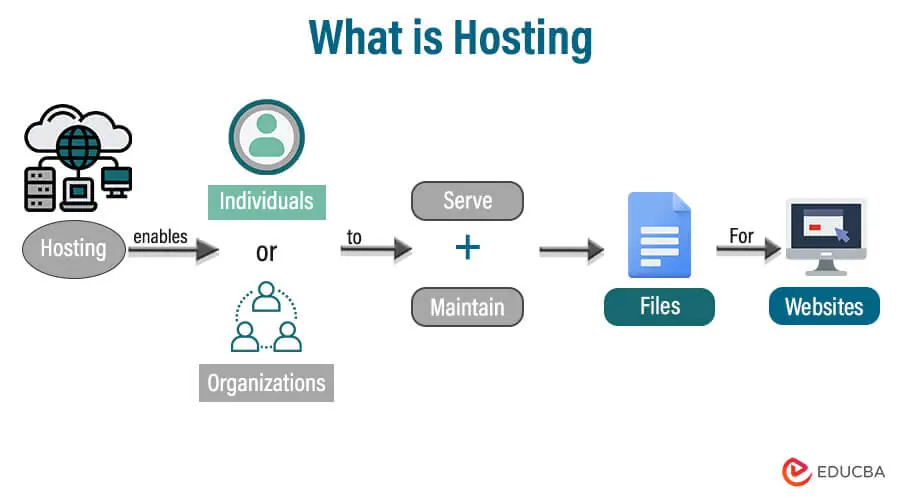
Hosting refers to the provision of infrastructure or services that allow individuals or organizations to make their websites, applications, or content accessible on the internet. Hosting services provide the necessary resources, such as servers, storage, and network connectivity, to store and deliver digital content to users worldwide. It plays a fundamental role in ensuring the online presence of websites and applications.
Analogy:
Think of hosting as renting space in a shopping mall. In the same way a store rents space in a mall to display and sell its products, websites rent space on servers to showcase their digital content and make it accessible to visitors on the internet.
Further Description:
Hosting involves various elements:
Types of Hosting:
- Shared Hosting: Multiple websites share resources on the same server.
- VPS (Virtual Private Server) Hosting: A virtualized server environment where each website has its dedicated resources.
- Dedicated Hosting: A dedicated server exclusively for one website or application.
- Cloud Hosting: Hosting on a network of interconnected virtual and physical servers.
Server Management:
- Configuration: Setting up the server according to the website or application requirements.
- Maintenance: Regular updates, security patches, and performance optimization.
- Monitoring: Continuous tracking of server health, resource usage, and potential issues.
Domain Management:
- Domain Registration: Acquiring and renewing domain names for websites.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Configuring domain settings to point to the correct server.
Security Measures:
- Firewalls: Implementing firewalls to protect against unauthorized access.
- SSL Certificates: Enabling secure connections through HTTPS.
- Backup Systems: Regularly backing up data to prevent loss in case of emergencies.
Scalability:
- Resource Scaling: Adjusting server resources based on website traffic and performance needs.
- Load Balancing: Distributing incoming traffic across multiple servers to prevent overload.
Why is Hosting Important?
Website Accessibility: Hosting ensures that websites and applications are available and accessible to users on the internet.
Performance and Speed: The quality of hosting influences the speed and performance of websites, impacting user experience.
Reliability and Uptime: A reliable hosting service minimizes downtime, ensuring websites are consistently available to users.
Security: Hosting services implement security measures to protect websites and user data from potential threats.
Scalability: Hosting allows websites to scale resources up or down based on changing needs, accommodating growth or fluctuations in traffic.
Examples and Usage:
- Bluehost: A popular shared hosting provider, Bluehost offers a range of hosting solutions for websites, including shared hosting, VPS hosting, and dedicated hosting.
Amazon Web Services (AWS): AWS provides cloud hosting services, offering a wide array of scalable and flexible solutions for businesses, including cloud storage and computing resources.
GoDaddy: Known for domain registration, GoDaddy also offers various hosting services, including shared hosting and managed WordPress hosting.
Key Takeaways:
- Shared, VPS, Dedicated, and Cloud hosting cater to different needs and resource requirements.
- Configuration, maintenance, monitoring, and security measures are crucial for effective hosting.
- Domain registration and DNS configuration are integral parts of hosting.
- Firewalls, SSL certificates, and backup systems contribute to the security of hosted content.
- Hosting allows for resource scaling and load balancing to adapt to changing demands.