Lean Startup Principles Application
What is the Lean Startup Principles Application?
Definition:
Lean Startup is a methodology designed to create and manage startups more efficiently by developing products that meet the needs of early customers and reducing market risks. It emphasizes rapid experimentation, customer feedback, and iterative product releases to build a sustainable business. This approach allows startups to quickly adapt to market demands and minimize waste.
Analogy:
Imagine Lean Startup principles as a gardener planting seeds. Instead of planting an entire field without knowing which plants will thrive, the gardener plants a few seeds, observes which ones grow best, and then nurtures those plants. Similarly, a Lean Startup focuses on smallscale testing and learning before scaling up, ensuring that resources are used effectively.
Further Description:
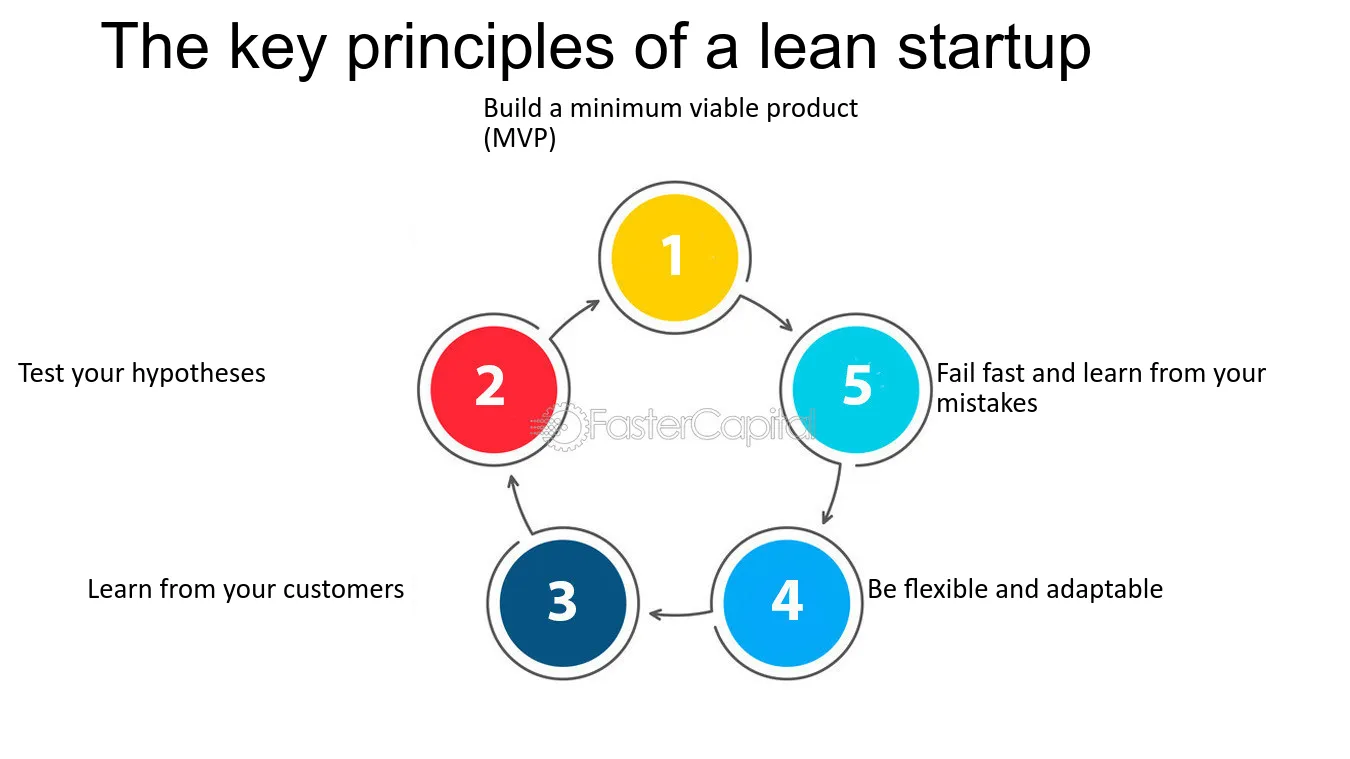
Lean Startup principles are built on several key concepts that guide the process of developing and scaling a startup:
BuildMeasureLearn:
This cycle is the core of the Lean Startup methodology. It involves building a minimum viable product (MVP), measuring its performance with real customers, and learning from the feedback to improve the product.
Build: Create an MVP with the minimal features necessary to test a hypothesis.
Measure: Collect data and feedback from users interacting with the MVP.
Learn: Analyze the data to determine if the hypothesis is valid or needs adjustment.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP):
MVP is a simplified version of a product that allows a team to collect the maximum amount of validated learning about customers with the least effort. It is designed to test assumptions and gather feedback early in the development process.
Validated Learning:
This concept involves testing hypotheses about a business model through experiments and obtaining factual data to confirm or refute the assumptions. It ensures that the startup is making informed decisions based on real customer behavior.
Pivot or Persevere:
Based on the feedback and data collected, startups decide whether to pivot (make a significant change in strategy) or persevere (continue with the current plan). This decision is critical in refining the business model and productmarket fit.
Innovation Accounting:
Innovation accounting focuses on measuring progress, setting up milestones, and prioritizing tasks that reduce the most significant risks. It involves using metrics that reflect true business progress, not vanity metrics that might look good but don’t drive success.
Key Components of Lean Startup Principles:
Customer Discovery: Engaging with potential customers to understand their needs and problems.
Hypothesis Testing: Formulating and testing assumptions about the product, market, and business model.
Rapid Prototyping: Quickly creating prototypes to test ideas and gather feedback.
Continuous Improvement: Iterating on the product based on user feedback and data analysis.
Metrics: Using actionable metrics to guide decisionmaking and measure progress.
Why are Lean Startup Principles Important?
Efficiency: Helps startups use resources more effectively by focusing on validated learning and reducing waste.
Flexibility: Allows startups to adapt quickly to changes in the market or customer preferences.
Risk Reduction: Minimizes the risk of building a product that no one wants by validating assumptions early.
Customer Focus: Ensures that the product development is aligned with real customer needs and problems.
Scalability: Builds a foundation for scaling the business based on proven and validated insights.
Examples and Usage:
Dropbox: Used an MVP in the form of a video demonstration to validate customer interest before building the full product.
Airbnb: Tested the concept by renting out an air mattress in their apartment to see if there was demand for short term rentals.
Zappos: Started by testing if people would buy shoes online by setting up a basic website and fulfilling orders manually before investing in inventory.
Key Takeaways:
- Lean Startup principles help startups develop products that meet customer needs efficiently.
- The BuildMeasureLearn cycle is central to the methodology, emphasizing rapid experimentation and iterative development.
- Key components include MVPs, validated learning, and the pivot or persevere decision-making process.
- Lean Startup principles enhance efficiency, flexibility, risk reduction, customer focus, and scalability.
- Dropbox, Airbnb, and Zappos are examples of successful applications of Lean Startup principles.