Scalability
What is Scalability?
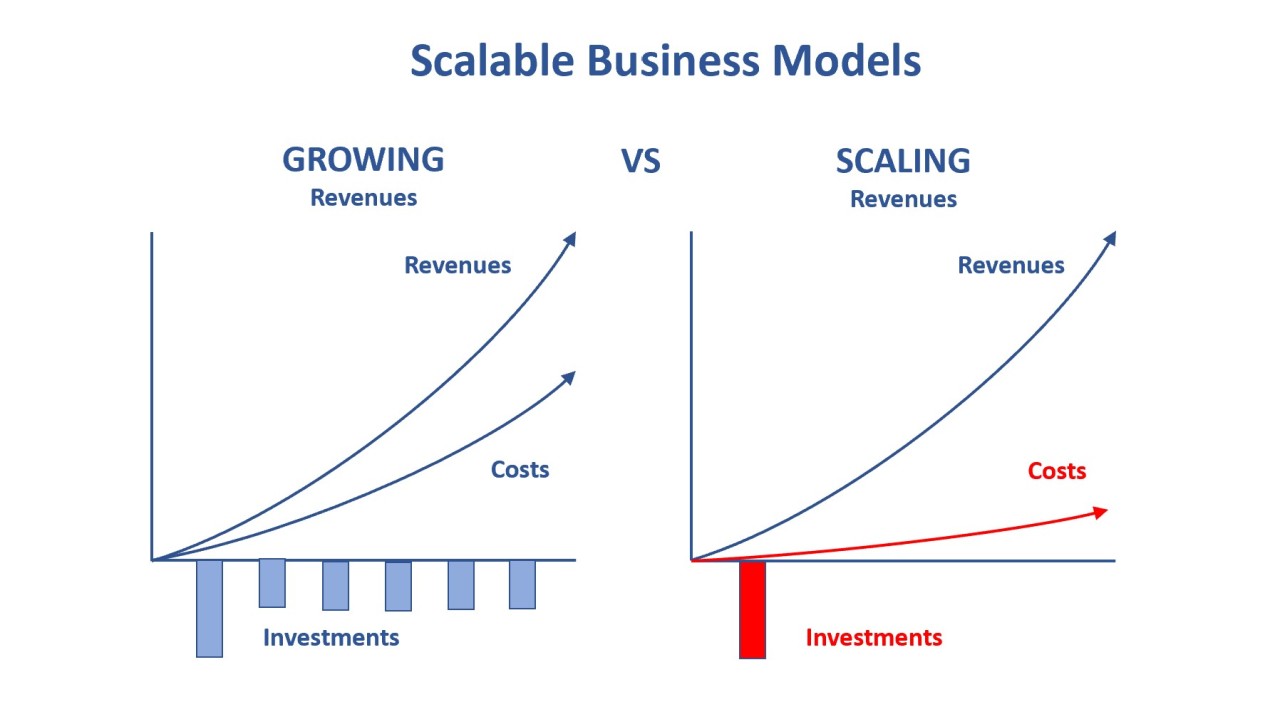
Definition:
Scalability in business refers to the capability of a system, process, or organization to handle growth, expansion, or increased demand while maintaining or improving its performance, efficiency, and effectiveness. It involves designing and implementing structures and strategies that allow a business to adapt seamlessly to changes in size or volume, whether it be in terms of customers, operations, or overall market reach.
Analogy:
Think of scalability as the ability of a business to effortlessly adjust its gears and mechanisms to accommodate a surge in demand or a significant increase in its scope. Just like a well-designed and scalable manufacturing plant that can seamlessly ramp up production when needed, scalable businesses can grow and evolve without compromising their core functionality.
Further Description:
Scalability encompasses various dimensions within a business, including:
- Operational Scalability: Involves enhancing processes and systems to efficiently handle an increase in workload without causing disruptions or diminishing performance.
- Technical Scalability: Focuses on the adaptability of a business’s technological infrastructure, ensuring that systems can handle growth in data, user traffic, and transactions without experiencing downtime or performance issues.
- Financial Scalability: Involves developing financial structures and strategies that can support business growth, such as securing additional funding, optimizing cost structures, and managing cash flow effectively.
- Market Scalability: Relates to a business’s ability to expand its market presence, reach new customer segments, and enter different geographical regions without losing efficiency or compromising the quality of its products or services.
Why is Scalability Important?
- Adaptability to Growth: Scalability allows businesses to grow organically or in response to market demands without facing significant operational hurdles.
- Resource Optimization: Scalable businesses can optimize resources effectively, preventing overextension during periods of growth and adapting to fluctuations in demand.
- Competitive Advantage: Scalability positions businesses to be more agile and responsive, giving them a competitive edge in dynamic and evolving markets.
- Enhanced Resilience: Scalable structures enhance a business’s ability to withstand economic uncertainties and market fluctuations by providing the flexibility to adjust to changing circumstances.
Examples and Usage:
Cloud Computing Services: Businesses leverage scalable cloud platforms to expand or contract their computing resources based on demand, ensuring optimal performance and cost efficiency.
E-commerce Platforms: Scalable e-commerce websites can handle increased traffic during sales or promotional events without experiencing slowdowns or crashes.
Flexible Workforce Models: Companies adopting scalable workforce models, such as remote or flexible work arrangements, can quickly adjust to changes in staffing needs.
Key Takeaways:
Multifaceted Nature: Scalability involves adaptability in operations, technology, finance, and market presence.
Strategic Planning: Scalability requires strategic planning and the implementation of flexible structures to accommodate growth seamlessly.
Business Resilience: Scalability contributes to a business’s resilience, enabling it to navigate challenges and capitalize on opportunities effectively.
Examples of Scalability: Cloud computing, e-commerce platforms, and flexible workforce models illustrate how businesses can achieve scalability in various aspects of their operations.




