SWOT Analysis
What is SWOT Analysis
Definition:
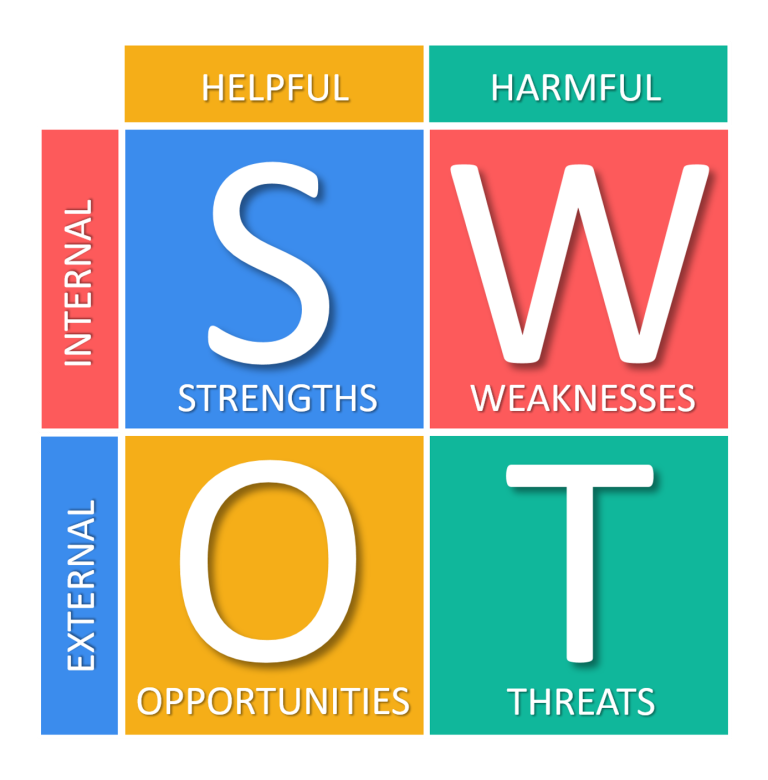
A SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used by businesses to assess internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. The acronym “SWOT” stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. By conducting a SWOT analysis, organizations can gain valuable insights into their current position in the market and develop strategies to capitalize on strengths, mitigate weaknesses, exploit opportunities, and mitigate threats.
Analogy:
Think of a SWOT analysis as a compass that helps navigate a company through the ever-changing landscape of the business environment. Just as a compass provides direction by indicating the four cardinal points, a SWOT analysis guides decision-making by identifying internal factors (strengths and weaknesses) and external factors (opportunities and threats) that influence the organization’s trajectory.
Further Description:
A SWOT analysis involves a structured assessment of the following elements:
Strengths: Internal factors that give the organization a competitive advantage and contribute to its success. This may include unique resources, strong brand reputation, skilled workforce, or proprietary technology.
Weaknesses: Internal factors that place the organization at a disadvantage or hinder its performance. Weaknesses may include inadequate resources, poor infrastructure, lack of innovation, or inefficient processes.
Opportunities: External factors in the business environment that present favorable conditions for growth, expansion, or improvement. Opportunities may arise from market trends, technological advancements, changes in consumer behavior, or emerging markets.
Threats: External factors that pose risks or challenges to the organization’s viability and competitiveness. Threats may include increased competition, economic downturns, regulatory changes, shifts in consumer preferences, or disruptive technologies.
Why is SWOT Analysis Important?
Strategic Planning: SWOT analysis provides a systematic framework for strategic planning, enabling organizations to align their resources and capabilities with external opportunities and threats.
Risk Management: By identifying weaknesses and threats, organizations can develop proactive strategies to mitigate risks and minimize potential negative impacts on their operations.
Decision Making: SWOT analysis informs decision-making processes by highlighting key areas of focus and guiding resource allocation towards areas of greatest potential.
Competitive Advantage: Understanding strengths and opportunities allows organizations to leverage their competitive advantages and differentiate themselves from competitors.
Examples and Usage:
Product Development: Before launching a new product, companies conduct a SWOT analysis to assess market demand, competitive landscape, and internal capabilities.
Strategic Planning: During annual planning sessions, businesses perform SWOT analyses to evaluate their current position and chart a course for future growth and development.
Market Entry: Before entering a new market or expanding into different regions, organizations analyze the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats to determine the feasibility and potential success of the venture.
Key Takeaways:
- A SWOT analysis helps organizations assess internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats.
- It informs strategic decision-making, risk management, and resource allocation.
- Key elements include strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Examples of SWOT analysis applications include product development, strategic planning, and market entry strategies.