Talent Management
What is Talent Management
Definition:
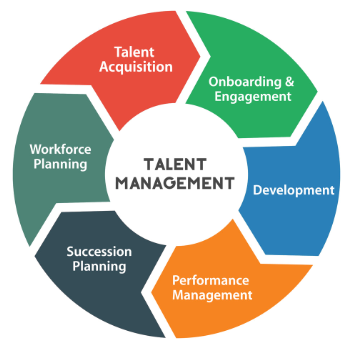
Talent management refers to the strategic process of attracting, developing, retaining, and optimizing the skills and capabilities of employees within an organization. It encompasses various activities aimed at aligning talent with business objectives and ensuring the organization has the right people in the right roles to drive success.
Analogy:
Imagine talent management as a gardener tending to a diverse array of plants in a garden. Just as a gardener nurtures plants to flourish and thrive, talent management involves nurturing employees’ skills, capabilities, and potential to maximize their contribution to the organization’s growth and success.
Further Description:
Talent management comprises several interconnected processes and practices, including:
Recruitment and Selection: Attracting and hiring individuals with the requisite skills, knowledge, and values to fulfill organizational needs and goals.
Performance Management: Setting clear performance expectations, providing feedback, and evaluating employee performance to recognize achievements and address areas for improvement.
Learning and Development: Providing opportunities for continuous learning, skill enhancement, and career development to help employees reach their full potential and contribute effectively to organizational objectives.
Succession Planning: Identifying and developing potential successors for key leadership positions to ensure continuity and mitigate risks associated with talent gaps.
Employee Engagement and Retention: Fostering a positive work environment, promoting open communication, and implementing strategies to enhance employee satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.
Why is Talent Management Important?
Strategic Alignment: Effective talent management aligns individual capabilities and aspirations with organizational objectives, ensuring that talent contributes to the achievement of business goals.
Competitive Advantage: A well-executed talent management strategy can serve as a source of competitive advantage by fostering a skilled, engaged workforce capable of driving innovation, productivity, and customer satisfaction.
Organizational Agility: Talent management enables organizations to adapt to changing market dynamics and emerging opportunities by cultivating a flexible, responsive workforce capable of meeting evolving business needs.
Employee Development: By investing in employee development and career advancement opportunities, talent management helps attract, motivate, and retain top talent while enhancing individual and organizational performance.
Examples and Usage:
Leadership Development Programs: Organizations implement leadership development initiatives to identify and nurture high-potential employees, preparing them for future leadership roles within the company.
Employee Training and Development: Companies offer various training programs, workshops, and educational opportunities to enhance employees’ skills, knowledge, and competencies in alignment with organizational goals.
Performance Management Systems: Organizations utilize performance management systems to set objectives, provide regular feedback, assess performance, and recognize and reward employees’ contributions.
Key Takeaways:
- Talent management involves strategically managing the full lifecycle of employees, from recruitment and selection to development, engagement, and retention.
- Core components include recruitment, performance management, learning and development, succession planning, and employee engagement.
- Benefits of effective talent management include strategic alignment, competitive advantage, organizational agility, and employee development.
- Examples of talent management practices include leadership development programs, employee training, and performance management systems.
Table of Contents