Traction
What is Traction?
Definition:
Traction in a business context refers to the measurable progress and momentum achieved by a company in terms of customer acquisition, revenue growth, and market penetration. It signifies the ability of a business to gain a foothold in the market, attract customers, and demonstrate a positive trajectory toward its goals. Traction is often used as a key indicator of a company’s viability and potential for success.
Analogy:
Imagine traction as the steady acceleration of a vehicle on a well-maintained road. Just as a vehicle gains traction to move forward smoothly, a business gains traction by effectively attracting and retaining customers, generating revenue, and expanding its presence in the market.
Further Description:
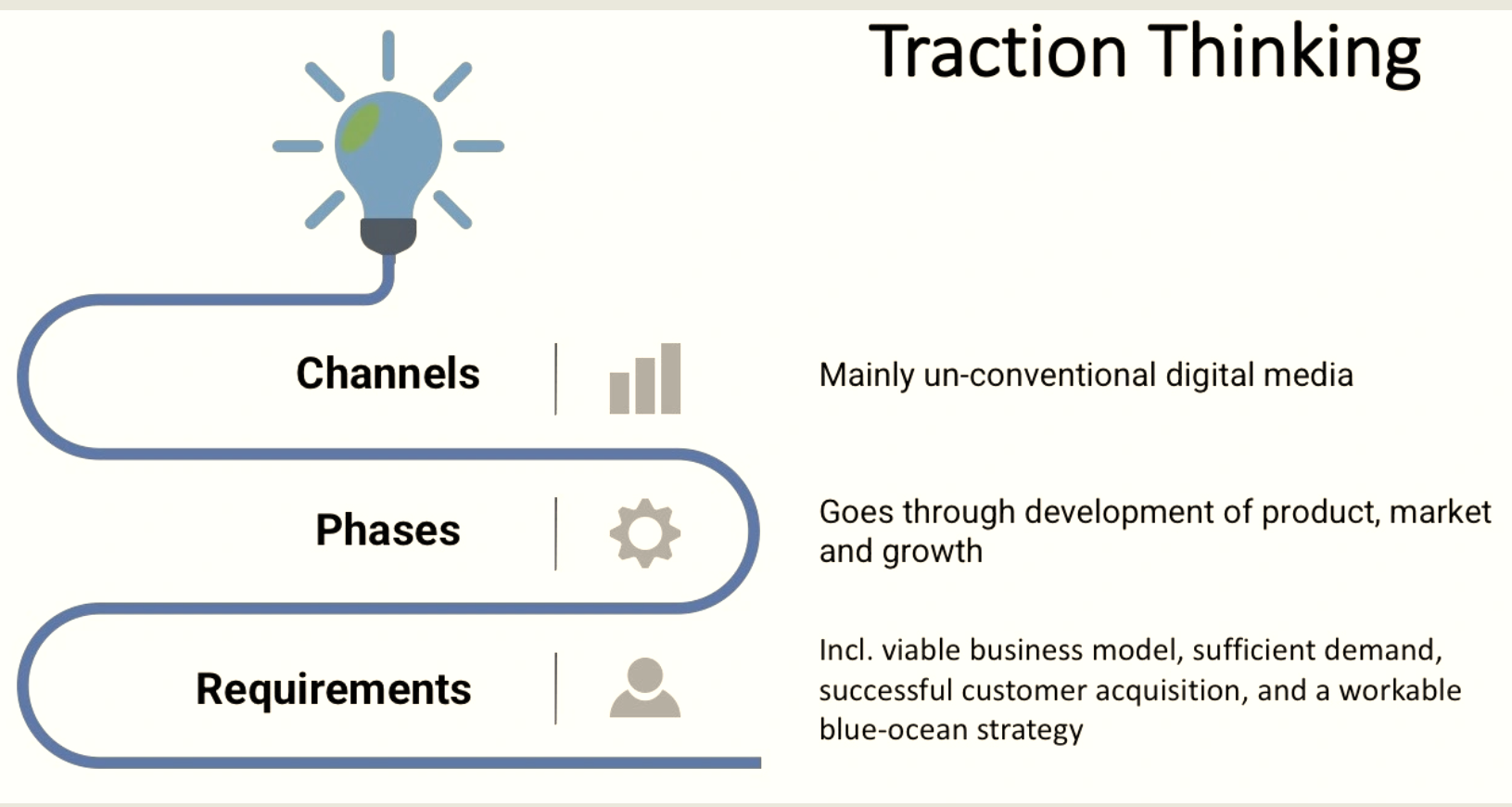
Traction encompasses several key elements within a business’s journey, including:
Customer Acquisition: The process of attracting and onboarding new customers to the product or service, demonstrating a growing customer base.
Revenue Growth: Increasing the overall revenue generated by the business through sales, partnerships, and other income streams.
Market Penetration: Expanding the business’s presence within the target market and gaining a larger share of the customer base.
User Engagement: Building and maintaining a loyal customer base through positive user experiences and effective engagement strategies.
Why is Traction Important?
Validation of Business Model: Traction serves as evidence that the business has a viable product or service that resonates with the target audience, validating the underlying business model.
Attracting Investors: Investors often look for businesses with traction as it indicates potential for return on investment and reduces perceived risk.
Competitive Edge: Traction allows a business to establish itself in the market, creating a competitive advantage over other players.
Customer Confidence: Positive traction builds confidence among customers, signaling that the business is reliable and provides value.
Examples and Metrics:
Customer Acquisition Rate: Measuring the rate at which new customers are acquired over a specific period.
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR): Tracking the predictable and recurring revenue generated by the business on a monthly basis.
Market Share Growth: Assessing the increase in the business’s market share relative to competitors.
User Retention Rate: Evaluating the ability of the business to retain existing customers over time.
Key Takeaways:
- Traction is the measurable progress and momentum a business achieves in terms of customer acquisition, revenue growth, and market penetration.
- It validates the business model, attracts investors, and provides a competitive edge.
- Metrics such as customer acquisition rate, MRR, market share growth, and user retention rate help assess traction.
- Successful businesses strategically navigate and accelerate their growth by gaining meaningful traction in the market.