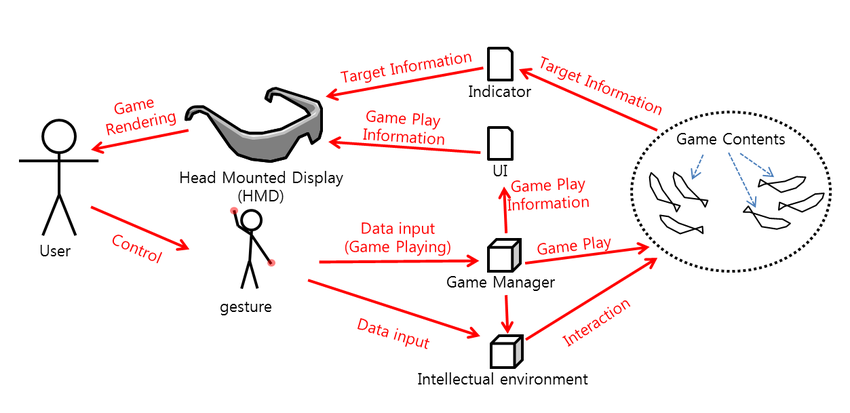
Virtual Reality (VR)
What is Virtual Reality (VR)
Definition:
Virtual Reality (VR) is a computer-generated environment that simulates a realistic or imaginary three-dimensional experience, often using special electronic equipment such as headsets or gloves. VR immerses users in a digital world, allowing them to interact with and experience the environment as if it were real. This technology is widely used for entertainment, gaming, education, training, and various professional applications.
Analogy:
Think of Virtual Reality as a portal to alternate realms. Similar to how a book or movie transports you to a different world, VR takes immersion to the next level by making you an active participant in a three-dimensional space. It’s like stepping through a magical doorway into a digital universe, where your senses perceive and respond to a computer-generated reality.
Further Description:
Virtual Reality involves several key components and functionalities, including:
Hardware Devices: VR headsets, gloves, and motion controllers are key components that enable users to see, hear, and interact with the virtual environment.
Immersive Environments: VR creates realistic or fantastical worlds that users can explore. These environments are often created using 3D modeling, animation, and spatial audio technologies.
Interactive Experiences: VR allows users to actively engage with the virtual world. They can manipulate objects, navigate spaces, and even communicate with other users in shared virtual spaces.
Motion Tracking: Sensors and cameras track users’ movements, allowing the virtual environment to respond to their actions in real-time. This enhances the feeling of presence within the digital space.
Why is Virtual Reality Important?
Immersive Learning: VR is a powerful tool for education and training, providing realistic simulations for various fields such as medicine, aviation, and emergency response.
Entertainment and Gaming: VR enhances gaming experiences by placing players directly into the game world, creating a more engaging and captivating entertainment medium.
Architectural Visualization: Professionals in architecture and design use VR to visualize and explore virtual representations of buildings and spaces before construction.
Therapeutic Applications: VR is utilized for therapeutic purposes, such as treating phobias, PTSD, and anxiety disorders through exposure therapy in a controlled virtual environment.
Examples and Usage:
VR Gaming: Popular VR games like Beat Saber, Half-Life: Alyx, and VR adaptations of traditional games offer immersive and interactive entertainment experiences.
Medical Training: Surgeons use VR simulations for surgical training, allowing them to practice procedures in a risk-free virtual environment.
Real Estate: Virtual tours and simulations enable potential buyers to explore properties remotely, enhancing the property viewing experience.
Key Takeaways:
- Virtual Reality creates a computer-generated environment that users can interact with and experience.
- Hardware and Software Integration: VR relies on specialized hardware devices and software to provide a seamless and immersive user experience.
- Wide Range of Applications: From gaming and entertainment to education and therapy, VR has diverse applications across various industries.
- Enhanced Interactivity: Users can actively engage with and manipulate objects in the virtual world, creating a sense of presence and immersion.
Table of Contents