Crowdsourcing
What is Crowdsourcing?
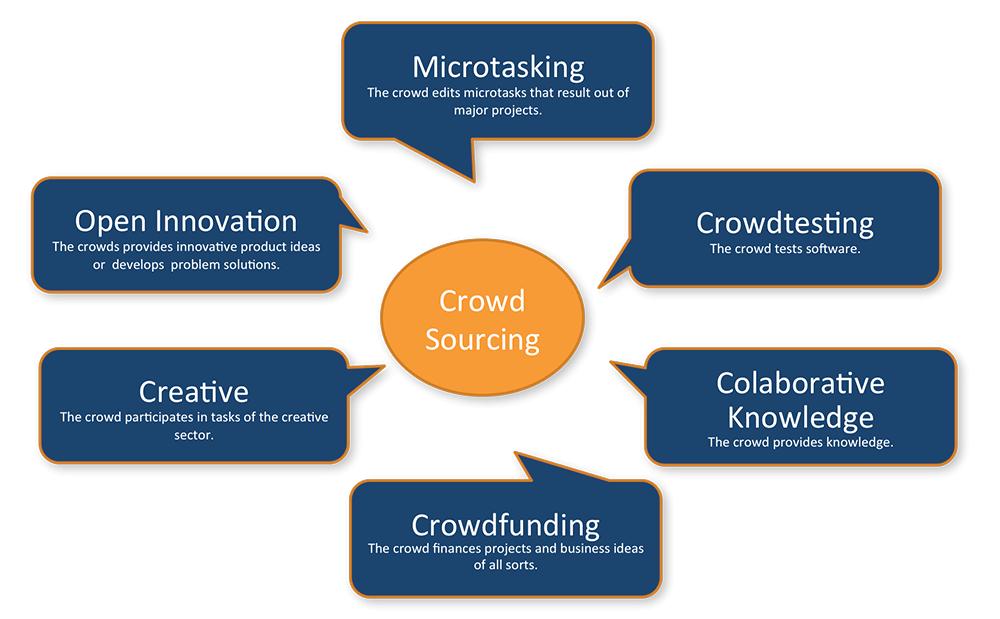
Definition:
“Crowdsourcing” is a business practice that involves obtaining ideas, services, or content by soliciting contributions from a large group of people, typically an online community. It harnesses the collective intelligence, skills, or resources of a diverse crowd to address specific challenges, solve problems, or generate innovative solutions. Crowdsourcing can take various forms, including idea generation, data collection, design contests, and collaborative problem-solving.
Analogy:
Imagine assembling a team of experts from different fields to collaborate on a project. Crowdsourcing, in a similar way, involves tapping into the collective expertise and creativity of a diverse group, often on a global scale, to achieve a common goal.
Further Description:
Crowdsourcing leverages the power of the crowd to source information, ideas, or contributions. It has become more prevalent with the advent of digital platforms and social media, enabling organizations to reach a broader audience. Crowdsourcing can be used for tasks such as product development, market research, content creation, and problem-solving. Platforms and tools dedicated to crowdsourcing facilitate the interaction between organizations and participants, making it easier to manage large-scale collaboration.
Why is Crowdsourcing Important?
Crowdsourcing offers several advantages, including access to a diverse pool of talent, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to generate innovative solutions. It fosters engagement with a community of contributors, enabling organizations to tap into a collective intelligence that may not be available within their internal teams. Crowdsourcing is particularly valuable for projects that benefit from a wide range of perspectives, skills, or creative input.
Examples and Usage:
Idea Generation: Companies may use crowdsourcing to gather ideas for new products, features, or marketing campaigns from a diverse community of contributors.
Data Labeling: Crowdsourcing is employed for tasks such as data labeling, where contributors help annotate images, videos, or other datasets to train machine learning models.
Design Contests: Organizations may run design contests, allowing designers from around the world to submit their creations for logos, packaging, or other visual elements.
Citizen Science: Crowdsourcing is utilized in scientific research, with citizens contributing observations, data, or analyses to projects ranging from astronomy to environmental monitoring.
Basically, Crowdsourcing is a collaborative approach that involves obtaining ideas, services, or content by soliciting contributions from a large and diverse group of people, often facilitated through digital platforms.
For example, a company might use crowdsourcing to collect feedback on a new product, allowing customers and enthusiasts to share their insights and ideas.
Key Takeaways:
- Crowdsourcing is a business practice that involves obtaining ideas, services, or content by soliciting contributions from a large and diverse group of people.
- It harnesses the collective intelligence, skills, or resources of a crowd to address challenges, solve problems, or generate innovative solutions.
- Crowdsourcing can take various forms, including idea generation, data labeling, design contests, and citizen science.
- It offers advantages such as access to diverse talent, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to tap into collective intelligence.




