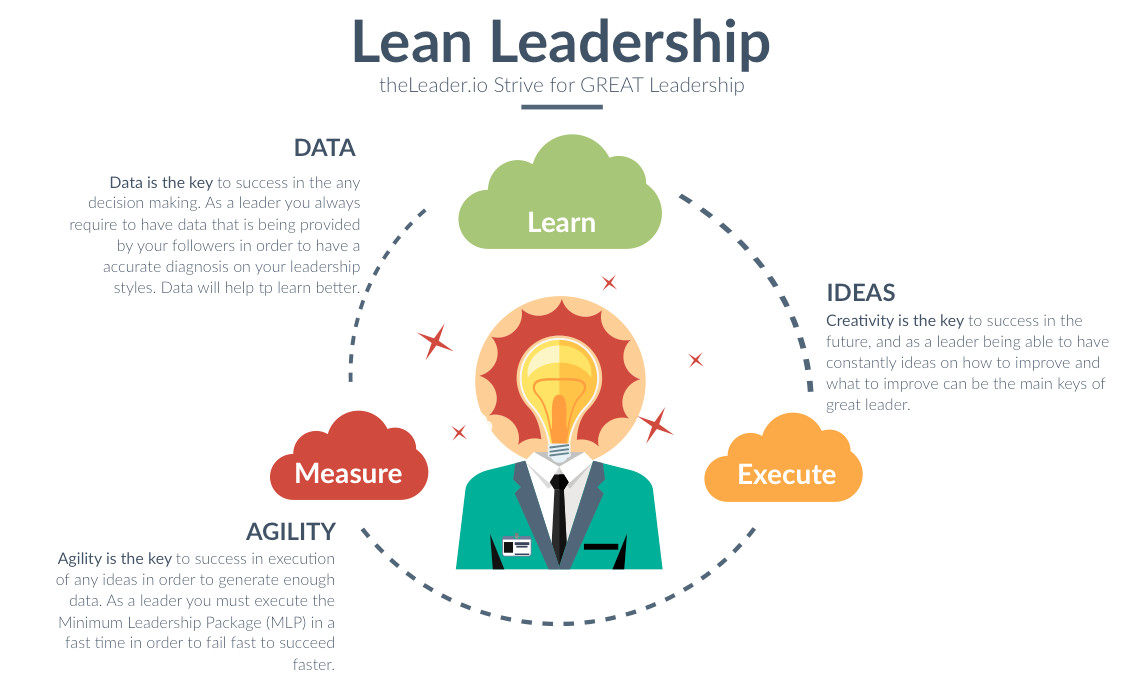
Lean Leadership
What is Lean Leadership?
Definition:
Lean leadership is an approach focused on maximizing value for customers while minimizing waste through continuous improvement, respect for people, and empowering teams. It draws its principles from the Lean methodology, originally developed by Toyota in the 20th century, and applies them to leadership practices in various organizational settings.
Analogy:
Think of lean leadership as the conductor of an orchestra. Just as a conductor guides individual musicians to perform harmoniously as a whole, lean leaders orchestrate their teams to work collaboratively towards shared goals, optimizing processes and resources along the way.
Further Description:
Lean leadership emphasizes the following key principles:
Value Stream Mapping: Identifying and understanding the entire value stream of a process to eliminate waste and create value for customers.
Continuous Improvement (Kaizen): Encouraging small, incremental changes and empowering employees at all levels to identify and solve problems to improve efficiency and effectiveness.
Respect for People: Valuing every individual within the organization, fostering a culture of trust, respect, and collaboration, and empowering employees to contribute their ideas and talents.
Visual Management: Making information about processes, performance, and goals visible and accessible to all team members, enabling better decision-making and alignment.
Just-in-Time (JIT): Minimizing inventory and lead times by producing only what is needed, when it is needed, to reduce waste and improve responsiveness to customer demand.
Key Components of Lean Leadership:
Vision and Strategy: Clear direction and goals that align with the organization’s purpose and values.
Empowerment: Delegating authority and responsibility to employees, trusting them to make decisions and take ownership of their work.
Coaching and Development: Providing support, feedback, and opportunities for growth to help employees develop their skills and reach their full potential.
Gemba Walks: Engaging with frontline employees to understand their work, identify opportunities for improvement, and demonstrate leadership presence and support.
Why is Lean Leadership Important?
Efficiency and Effectiveness: Lean leadership helps organizations streamline processes, reduce waste, and improve productivity, leading to better outcomes for customers and stakeholders.
Employee Engagement and Satisfaction: By empowering employees, fostering a culture of continuous improvement, and respecting their contributions, lean leadership can increase morale, motivation, and job satisfaction.
Adaptability and Resilience: Lean principles enable organizations to adapt to change more quickly, respond to customer needs and market dynamics, and build resilience in the face of uncertainty.
Sustainable Growth: Lean leadership promotes sustainable growth by focusing on long-term value creation, building capabilities, and fostering innovation and learning.
Examples and Usage:
Toyota: The originator of the Lean methodology, Toyota is known for its commitment to continuous improvement, respect for people, and lean leadership practices throughout its organization.
Zappos: The online retailer Zappos has embraced lean leadership principles to create a culture of empowerment, innovation, and customer focus.
SpaceX: Elon Musk’s aerospace company SpaceX applies lean principles to its operations, driving efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and rapid innovation in space exploration.
Key Takeaways:
- Lean leadership is an approach that applies lean principles to leadership practices, focusing on maximizing value, minimizing waste, and empowering teams.
- Key components include vision and strategy, empowerment, coaching and development, and gemba walks.
- Lean leadership is important for improving efficiency and effectiveness, engaging employees, adapting to change, and achieving sustainable growth.
- Toyota, Zappos, and SpaceX are examples of organizations that have successfully implemented lean leadership principles to drive performance and innovation.
Table of Contents