Lean Management
What is Lean Management?
Definition:
Lean Management is a systematic approach to running an organization by focusing on continuously improving processes, eliminating waste, and delivering value to customers. It is derived from the Toyota Production System (TPS) and emphasizes efficiency, quality, and respect for people.
Analogy:
Imagine Lean Management as a finely tuned orchestra. Just as each musician must play their part precisely to create a harmonious performance, every employee and process in an organization must work efficiently and in sync to achieve optimal results. The conductor, akin to Lean principles, ensures that everyone is aligned and working towards a common goal.
Further Description:
Lean Management can be applied to various industries and organizational functions, including manufacturing, services, healthcare, and more. Its core principles and methodologies aim to streamline operations and enhance productivity.
Core Principles of Lean Management:
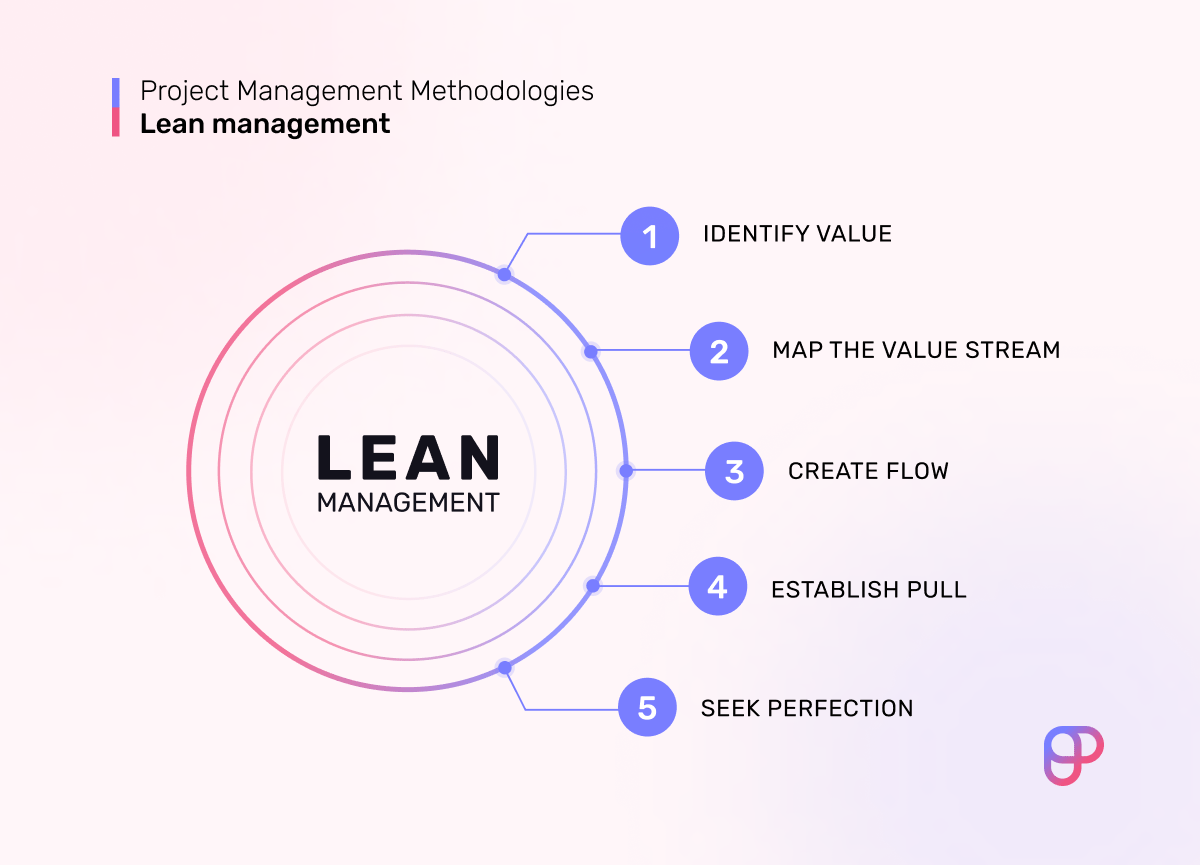
Value: Identify what the customer values and focus on delivering it.
Value Stream: Map out all steps in the value stream and eliminate those that do not add value.
Flow: Ensure that value flows smoothly without interruptions.
Pull: Produce only what is needed by the customer, reducing excess inventory and waste.
Perfection: Continuously improve processes to strive for perfection.
Types of Waste (Muda) in Lean Management:
Transportation: Unnecessary movement of products or materials.
Inventory: Excess products or materials not being processed.
Motion: Unnecessary movements by people.
Waiting: Idle time waiting for the next step in the process.
Overproduction: Producing more than what is needed.
Overprocessing: Doing more work than is necessary.
Defects: Efforts involved in inspecting and fixing errors.
Key Components of Lean Management:
Kaizen: A philosophy of continuous improvement where employees at all levels work together to achieve incremental changes.
5S Methodology: A workplace organization method involving Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
Kanban: A visual system for managing work as it moves through a process, ensuring just-in-time production.
Value Stream Mapping: A tool for analyzing and designing the flow of materials and information required to bring a product to the customer.
Standardized Work: Documented best practices for a process to ensure consistency and efficiency.
Why is Lean Management Important?
Efficiency: Streamlines processes to reduce waste and improve productivity.
Quality: Focuses on delivering high-quality products and services that meet customer needs.
Employee Engagement: Empowers employees to contribute to continuous improvement and problem-solving.
Cost Reduction: Reduces unnecessary costs associated with waste and inefficiencies.
Customer Satisfaction: Enhances the ability to deliver value, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Examples and Usage:
Toyota: The origin of Lean Management, known for its efficient production system and continuous improvement culture.
Nike: Implemented Lean principles in manufacturing to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
Healthcare: Hospitals use Lean to streamline patient care processes, reduce wait times, and improve service quality.
Software Development: Agile methodologies in software development incorporate Lean principles to enhance flexibility and responsiveness.
Key Takeaways:
- Lean Management is a continuous improvement philosophy focusing on eliminating waste and delivering value to customers.
- Key components include Kaizen, 5S, Kanban, Value Stream Mapping, and Standardized Work.
- Lean Management enhances efficiency, quality, employee engagement, cost reduction, and customer satisfaction.
- Examples of successful Lean Management implementation can be seen in companies like Toyota, Nike, and various healthcare organizations.