Lean Startup
What is a Lean Startup?
Definition:
The Lean Startup methodology is an entrepreneurial approach to business development that emphasizes rapid iteration, customer feedback, and a scientific approach to creating and managing startups. It was introduced by Eric Ries in his book “The Lean Startup” and has become a widely adopted framework for building and scaling startups. The core principles of the Lean Startup include validating assumptions through experimentation, building a minimum viable product (MVP), and adapting the business model based on real-time customer feedback.
Analogy:
Consider the Lean Startup approach as a scientific experiment. Just as scientists formulate hypotheses, conduct experiments, gather data, and adjust their theories based on the results, entrepreneurs using the Lean Startup methodology continually test and refine their business ideas through iterative cycles of learning and adaptation.
Further Description:
Lean Startup development involves several key components:
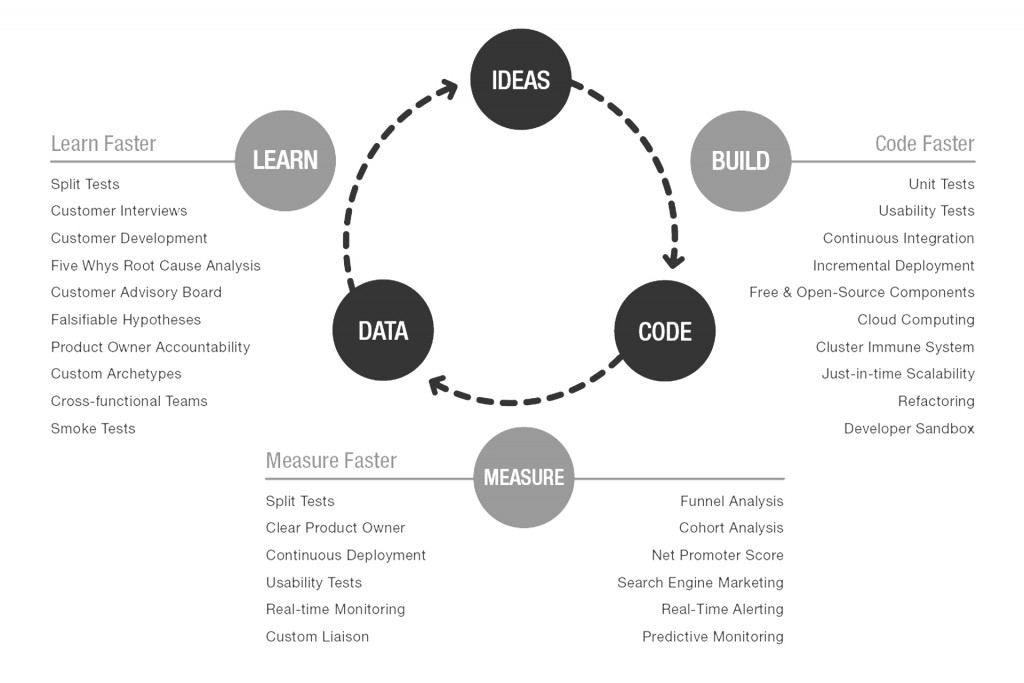
Build-Measure-Learn: The Lean Startup operates on a Build-Measure-Learn feedback loop. Entrepreneurs build a minimum viable product (MVP), measure its performance, learn from customer feedback, and then iterate or pivot based on the insights gained.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP): The concept of an MVP involves creating a simplified version of a product with the minimum features required to test its viability in the market. This allows startups to quickly gather feedback and avoid investing time and resources in building a full product that may not meet customer needs.
Validated Learning: The emphasis is on validated learning, where entrepreneurs systematically test hypotheses about their business model and value propositions. Learning from real-world data helps refine the product and business strategy.
Pivot or Persevere: Based on the insights gained from customer feedback and data analysis, entrepreneurs decide whether to pivot (make a fundamental change to the product or strategy) or persevere (continue with the current approach).
Continuous Deployment: The Lean Startup encourages frequent and small releases of product updates to gather feedback quickly. This allows for rapid adaptation to changing market conditions.
Customer Development: Customer development involves actively engaging with potential customers to understand their needs, preferences, and pain points. This process helps shape the product and ensures market fit.
Why is Lean Startup Important?
Risk Mitigation: The Lean Startup methodology helps mitigate risks by validating assumptions early in the development process, reducing the likelihood of investing resources in an unviable product.
Efficient Resource Allocation: By focusing on building an MVP and testing hypotheses, startups can allocate resources more efficiently, avoiding unnecessary expenses on features that may not be essential to customers.
Customer-Centric Approach: Lean Startup places a strong emphasis on understanding and addressing customer needs, ensuring that the product is developed based on real customer feedback rather than assumptions.
Faster Time to Market: The iterative nature of the Lean Startup accelerates the development process, enabling startups to bring products to market faster and stay ahead of competitors.
Examples and Usage:
Dropbox: Dropbox, a cloud storage service, started with a simple explainer video showcasing the concept before building the actual product. This allowed them to test demand and gather feedback before investing heavily in development.
Zappos: Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, began by testing the idea of selling shoes online through a simple website. The positive response validated the concept, and Zappos expanded its offerings.
Instagram: Instagram initially launched as an iOS-only photo-sharing app with a focus on simplicity and user engagement. It quickly gained traction, leading to subsequent iterations and updates based on user feedback.
Key Takeaways:
- The Lean Startup operates on a continuous loop of building a minimum viable product, measuring its performance, and learning from customer feedback.
- Start with a simplified version of the product to quickly test its viability in the market and gather valuable insights.
- Focus on systematic testing of hypotheses to ensure that decisions are based on real-world data rather than assumptions.
- Based on feedback and data, be willing to make significant changes (pivot) or continue with the current approach (persevere) to achieve product-market fit.
- Regularly release updates to gather feedback quickly and adapt to changing market conditions.
- Actively engage with customers to understand their needs and preferences, ensuring that the product aligns with market demands.
- Lean Startup is important for risk mitigation, efficient resource allocation, a customer-centric approach, and achieving a faster time to market.
- Examples include Dropbox, Zappos, and Instagram, showcasing how the Lean Startup methodology contributed to their success.