Lean Startup Method
What is the Lean Startup Method?
Definition:
The Lean Startup Method is an approach to creating and managing startups with a focus on rapidly developing and iterating products to meet customer needs. This method emphasizes validated learning, scientific experimentation, and iterative product releases to shorten product development cycles, measure progress, and gain valuable customer feedback. The goal is to create a sustainable business by building products that satisfy customer demands.
Analogy:
Imagine the Lean Startup Method as building a prototype car in a workshop. Instead of creating a full-featured car right away, the team builds a basic version and tests it on the track. They gather feedback, make adjustments, and continuously improve the car based on real-world performance and user input. This iterative process ensures the final product meets the needs of the drivers.
Further Description:
Core Principles:
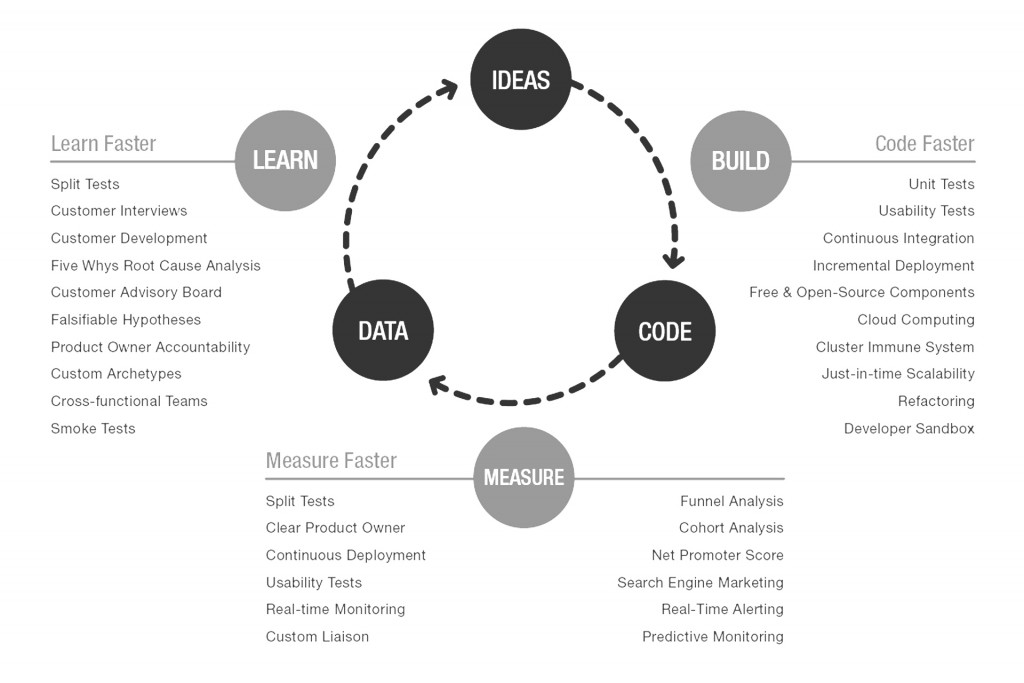
Build-Measure-Learn: This feedback loop is the foundation of the Lean Startup Method. Entrepreneurs start with building a Minimum Viable Product (MVP), measure its performance, learn from customer feedback, and iterate.
Validated Learning: Every iteration is an experiment to test a hypothesis about the product or market. Learning what works and what doesn’t is prioritized over traditional market research.
Pivot or Persevere: Based on the feedback and data collected, startups decide whether to pivot (make a fundamental change to the product or business model) or persevere (continue with the current strategy).
Types of Startups:
New Ventures: Newly founded businesses applying Lean principles from the outset.
Corporate Innovation: Established companies using Lean Startup techniques to innovate and develop new products.
Social Enterprises: Nonprofits and social ventures using Lean methods to maximize their impact and sustainability.
Key Components of Lean Startup:
Minimum Viable Product (MVP): The simplest version of the product that allows for maximum learning with the least effort.
Hypothesis Testing: Identifying and testing assumptions about the business model, market, and product.
Customer Development: Engaging with customers early and often to understand their needs and validate ideas.
Continuous Deployment: Releasing product updates frequently to improve based on user feedback.
Why is the Lean Startup Method Important?
Efficiency: Reduces wasted time and resources by focusing on building only what is necessary.
Customer-Centric: Ensures products are aligned with customer needs and market demand.
Adaptability: Enables startups to quickly pivot in response to market changes or new insights.
Risk Mitigation: Minimizes risks by testing hypotheses and validating ideas before large-scale investments.
Examples and Usage:
Dropbox: Started with a simple MVP—a demo video explaining the concept—which validated customer interest before developing the full product.
Zappos: Tested the hypothesis of selling shoes online by setting up a basic website and purchasing shoes from local stores to fulfill orders.
Buffer: Launched a minimal version of their social media scheduling tool to gather feedback and validate the need for the product before expanding its features.
Key Takeaways:
- The Lean Startup Method is an approach focused on rapid iteration, validated learning, and customer feedback.
- Key principles include Build-Measure-Learn, validated learning, and deciding when to pivot or persevere.
- Components like MVP, hypothesis testing, and continuous deployment are essential to the method.
- The method emphasizes efficiency, customer-centric development, adaptability, and risk mitigation.
- Successful examples include Dropbox, Zappos, and Buffer.
Table of Contents