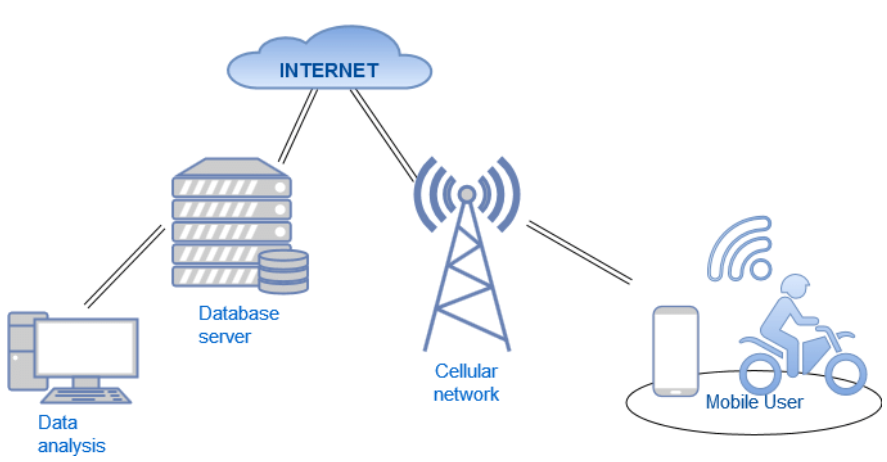
Local Server
What is a Local Server?
Definition:
A local server, also known as an on premises server, is a computing device or software application that provides services and resources within a local area network (LAN) environment. Unlike cloud based servers that operate over the internet, local servers are physically housed within an organization’s premises and are used to store, manage, and distribute data and applications to connected devices.
Analogy:
Think of a local server as a central hub in a neighborhood that stores and distributes resources to nearby households. Similar to how a neighborhood hub facilitates the sharing of resources among residents, a local server enables connected devices within a LAN to access shared files, applications, and services.
Further Description:
Local servers serve various functions within an organization, including:
Data Storage and Management: Local servers store and manage data files, databases, and documents for users and applications within the organization.
Application Hosting: Some local servers host applications and software programs that are accessed by users on the network, such as email servers, file servers, and intranet portals.
Print and File Sharing: Local servers facilitate file sharing and printing capabilities among networked devices, allowing users to collaborate and access shared resources.
Security and Access Control: Local servers implement security measures such as user authentication, access control lists, and data encryption to protect sensitive information and regulate access to resources.
Backup and Disaster Recovery: Local servers often serve as backup repositories for critical data and applications, enabling organizations to recover from data loss or system failures.
Why is a Local Server Important?
Control and Privacy: Hosting data and applications on a local server gives organizations greater control over their infrastructure and data privacy, reducing reliance on third party service providers.
Performance and Latency: Local servers typically offer faster data access and lower latency compared to cloud based solutions, especially for applications requiring real time processing or large data transfers.
Compliance Requirements: Certain industries and regulatory standards mandate data residency and compliance with specific security protocols, making local servers a preferred option for organizations with stringent compliance requirements.
Customization and Integration: Local servers can be customized and integrated with existing IT infrastructure and business processes, providing flexibility and interoperability tailored to organizational needs.
Examples and Usage:
File Servers: Local servers dedicated to storing and sharing files and documents among users within the organization.
Email Servers: Local servers hosting email services for internal communication and collaboration among employees.
Database Servers: Local servers managing databases and data storage for business applications, such as customer relationship management (CRM) systems and enterprise resource planning (ERP) software.
Key Takeaways:
- A local server is a computing device or software application that provides services and resources within a local area network (LAN) environment.
- Functions include data storage, application hosting, print and file sharing, security, backup, and disaster recovery.
- Benefits encompass control, privacy, performance, compliance, customization, and integration.
- Examples of local server usage include file servers, email servers, and database servers deployed within organizations.
Table of Contents