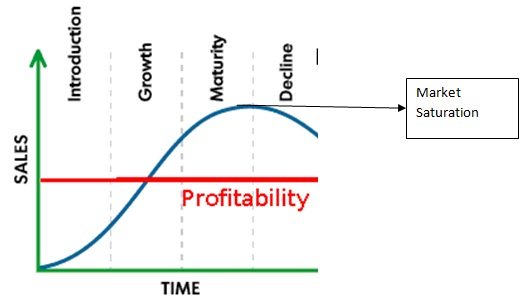
Market Saturation
What is Market Saturation
Definition:
Market saturation refers to a situation in which the demand for a product or service has reached its peak, and further expansion becomes challenging due to limited growth opportunities. It implies that most potential customers who are willing and able to purchase the product or service have already done so, leading to stagnant or declining sales growth.
Analogies:
Think of market saturation as a crowded room where every available space is occupied. Just as a crowded room has no space for additional occupants, a saturated market has limited room for new customers or products to enter and thrive.
Further Description:
Market saturation occurs when a product or service has achieved widespread adoption among its target audience, and there are few untapped segments or potential customers remaining. Factors contributing to market saturation include intense competition, declining product differentiation, market maturity, and changing consumer preferences.
Indicators of Market Saturation:
Slow Growth Rates: Market saturation is often characterized by sluggish or declining growth rates, as the market reaches its maximum potential and new customer acquisition becomes increasingly challenging.
High Competition: Saturated markets tend to have intense competition, with numerous players vying for market share and struggling to differentiate their offerings effectively.
Price Pressures: In saturated markets, price competition intensifies as companies seek to attract customers by offering discounts, promotions, and price incentives, leading to margin pressures and reduced profitability.
Declining Margins: As competition increases and differentiation diminishes, companies may experience declining profit margins as they lower prices to maintain market share and stimulate demand.
Challenges and Opportunities:
While market saturation presents challenges for companies seeking to grow within existing markets, it also creates opportunities for innovation, diversification, and expansion into new markets or product categories. Companies can explore strategies such as:
Product Innovation: Introducing innovative products or services with unique features, functionalities, or value propositions can reignite consumer interest and drive growth in saturated markets.
Market Segmentation: Identifying niche segments or underserved customer needs within saturated markets allows companies to tailor offerings and marketing strategies to specific customer segments, fostering loyalty and differentiation.
Diversification: Exploring diversification strategies, such as expanding into new geographic markets, complementary product categories, or adjacent industries, enables companies to reduce reliance on saturated markets and tap into new growth opportunities.
Value-Added Services: Offering value-added services, such as superior customer support, extended warranties, or loyalty programs, enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty, enabling companies to maintain market share and profitability despite saturation.
Key Takeaways:
- Market saturation occurs when the demand for a product or service reaches its peak, leading to limited growth opportunities and intense competition within the market.
- Indicators of market saturation include slow growth rates, high competition, price pressures, and declining margins, signaling the need for companies to explore innovative strategies to sustain growth and profitability.
- While market saturation poses challenges for companies operating within saturated markets, it also presents opportunities for innovation, diversification, and expansion into new markets or product categories, enabling companies to unlock new sources of growth and competitive advantage in dynamic market landscapes.
Table of Contents