Predictive Analytics
What is Predictive Analytics?
Definition:
Predictive Analytics involves the use of statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze historical data, identify patterns, and make predictions about future outcomes. It leverages data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning models to assess the likelihood of future events, enabling organizations to make informed decisions and optimize their strategies.
Analogy:
Think of predictive analytics as a weather forecasting system. Just as meteorologists analyze historical weather patterns and current conditions to predict future weather, predictive analytics analyzes past data to forecast future trends, behaviors, or outcomes.
Further Description:
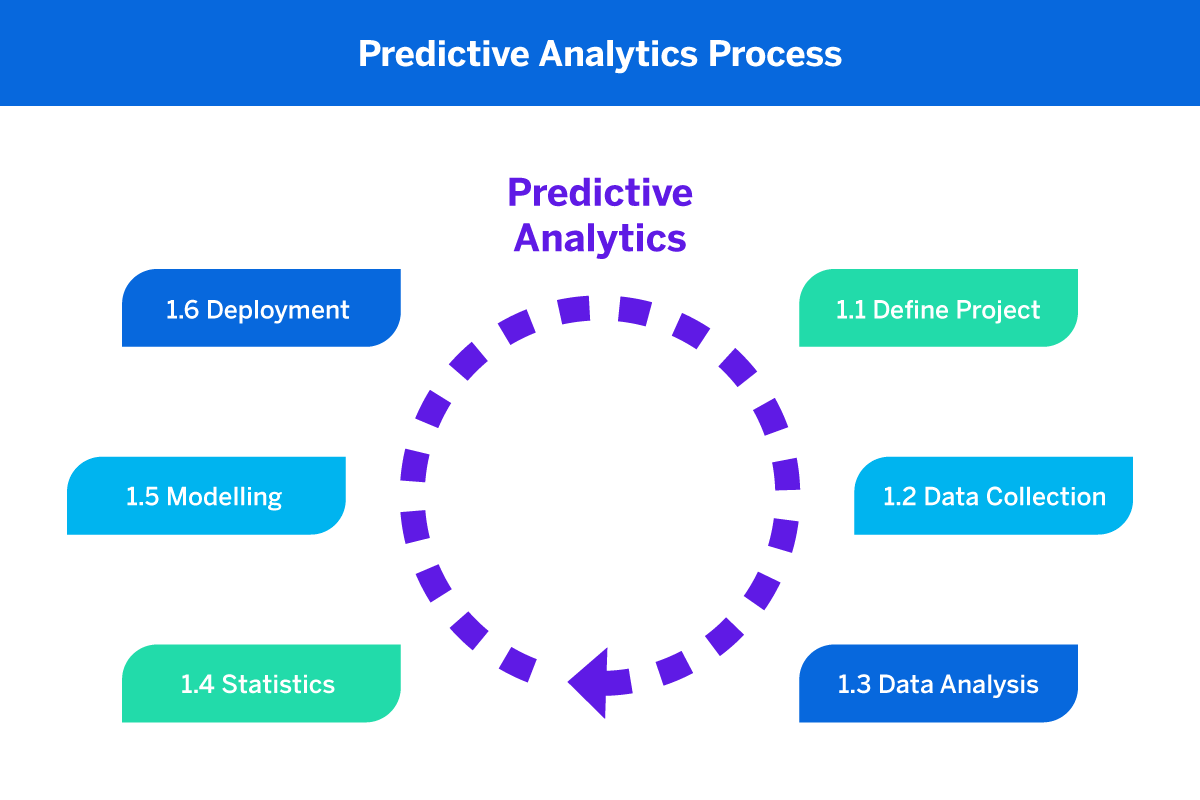
Predictive analytics development involves several key components:
Data Collection: Gathering relevant data from various sources, including historical records, customer interactions, and external data sets.
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Ensuring data accuracy and preparing it for analysis by addressing missing values, outliers, and other inconsistencies.
Feature Selection: Identifying the most relevant variables (features) that contribute to the predictive model’s accuracy.
Model Building: Developing and training predictive models using machine learning algorithms to learn patterns from historical data.
Validation and Testing: Assessing the model’s performance by validating it on new data sets and testing its ability to make accurate predictions.
Deployment: Integrating predictive models into business processes or applications for real-time decision-making.
Why is Predictive Analytics Important?
Informed Decision-Making: Predictive analytics provides valuable insights that help organizations make data-driven decisions, reducing uncertainty and improving strategic planning.
Risk Management: Businesses can use predictive analytics to identify potential risks and take proactive measures to mitigate them, minimizing negative impacts.
Personalization: By predicting customer behavior, organizations can tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to individual preferences, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Operational Efficiency: Predictive analytics helps optimize operations by forecasting demand, improving resource allocation, and streamlining processes.
Financial Planning: Predictive models aid in financial forecasting, budgeting, and resource allocation, contributing to better financial planning and management.
Examples and Usage:
Amazon Recommendations: Amazon uses predictive analytics to recommend products based on a customer’s browsing and purchase history, increasing the likelihood of sales.
Healthcare Diagnostics: Predictive analytics is employed in healthcare for patient risk stratification, predicting disease outbreaks, and optimizing treatment plans.
Credit Scoring: Financial institutions use predictive analytics to assess credit risk, predicting the likelihood of loan defaults based on historical data and individual credit profiles.
Key Takeaways:
- Predictive analytics empowers organizations to make informed decisions based on data and statistical models.
- It helps identify and mitigate potential risks, enhancing overall business resilience.
- Predictive analytics enables personalized experiences for customers by anticipating their preferences and behaviors.
- Organizations can streamline operations, allocate resources efficiently, and improve overall business processes through predictive analytics.