Product Development Lifecycle
What is the Product Development Lifecycle?
Definition:
The Product Development Lifecycle (PDLC) is a systematic process that guides the creation, design, development, and deployment of a new product. It encompasses the entire journey from the initial ideation phase to the product’s end-of-life. The PDLC involves a series of stages, each with specific activities and goals, to ensure a well-organized and efficient development process.
Analogy:
Think of the Product Development Lifecycle as a road trip. Just as a road trip involves careful planning, navigation, and adapting to unexpected twists and turns, the PDLC guides the journey of turning an idea into a tangible, market-ready product.
Further Description:
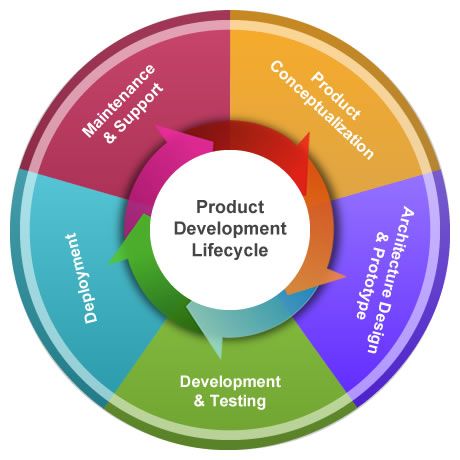
Product Development Lifecycle consists of several key stages:
- Idea Generation: This is the starting point, where ideas are brainstormed and evaluated. It involves market research, identifying customer needs, and exploring innovative concepts.
- Concept Development and Screening: Selected ideas are developed into viable concepts. Screening involves evaluating concepts against criteria such as feasibility, market potential, and alignment with business goals.
- Business Analysis: A detailed analysis of the proposed product’s viability is conducted. This includes cost estimation, market research, revenue projections, and a comprehensive business plan.
- Product Development: This stage involves turning the concept into a tangible product. It includes design, prototyping, coding (for software), and manufacturing (for physical products).
- Testing and Quality Assurance: The product undergoes rigorous testing to identify and fix any issues. Quality assurance ensures that the product meets specified standards and requirements.
- Market Launch: The product is introduced to the market. This includes marketing strategies, setting pricing, and developing distribution channels.
- Market Growth: The product gains traction, and efforts are focused on expanding market share, addressing customer feedback, and refining marketing strategies.
- Maturity: The product reaches a stable phase where sales and growth stabilize. Innovations may be introduced to extend the product’s lifecycle.
- Decline: Sales and market share decrease, and the product reaches the end of its lifecycle. Companies may decide to phase it out or introduce a successor.
Why is Product Development Lifecycle Important?
- Structured Approach: The PDLC provides a structured and organized approach to product development, ensuring that each stage is systematically addressed.
- Risk Management: By breaking down the development process into stages, potential risks can be identified and addressed early in the lifecycle, minimizing the impact on the final product.
- Resource Allocation: The PDLC helps in efficient allocation of resources by focusing efforts on the most critical aspects of development at each stage.
- Market Responsiveness: A well-defined PDLC allows for quicker responses to market changes and customer feedback, enabling timely adjustments to the product.
- Continuous Improvement: Through feedback loops and iterative processes, the PDLC supports continuous improvement, fostering innovation and product evolution.
Examples and Usage:
- Apple iPhone: Apple’s product development lifecycle for the iPhone involves meticulous planning, design, and continuous iteration. Each new iPhone release follows a structured development process to ensure innovation and market success.
- Tesla Electric Vehicles: Tesla’s product development lifecycle includes groundbreaking innovations in electric vehicles. From concept development to manufacturing, Tesla maintains a strong focus on technological advancements and sustainability.
- Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC): In the realm of software, companies like Microsoft follow a well-defined SDLC, including stages like planning, design, coding, testing, and deployment, to ensure the quality and functionality of software products.
Key Takeaways:
– Structured Approach: The PDLC provides a systematic and structured approach to product development.
– Risk Management: It allows for the identification and mitigation of potential risks throughout the development process.
– Resource Efficiency: Efficient allocation of resources is facilitated by focusing efforts on critical aspects at each stage.
– Market Responsiveness: The PDLC enables quick responses to market changes and customer feedback.
– Continuous Improvement: Through feedback loops, the PDLC supports continuous innovation and product evolution.
These key takeaways underscore the importance of a well-defined Product Development Lifecycle, emphasizing its role in ensuring a structured, efficient, and successful journey from idea generation to product launch and beyond.