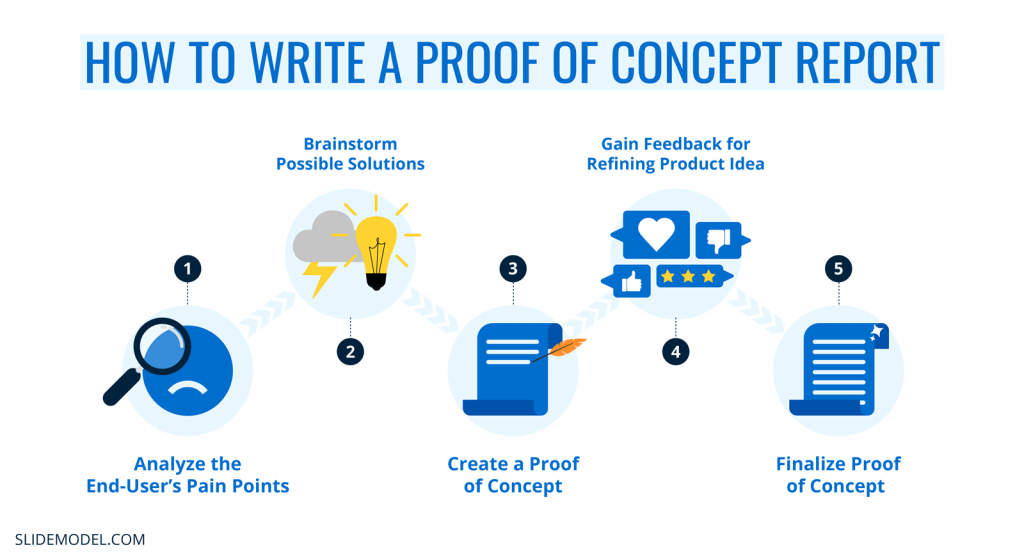
Proof of Concept
What is a Proof of Concept?
Definition:
A “Proof of Concept” (POC) in the realm of product development and innovation refers to a demonstration or prototype that validates the feasibility and potential of a new idea, technology, or solution. A POC aims to provide evidence that a concept or innovation can be successfully implemented and deliver the desired outcomes in a real-world environment.
Analogy:
Think of a Proof of Concept as a pilot episode of a TV series. Just as a pilot episode serves as a test run to gauge audience interest, gather feedback, and assess the viability of a show before committing to a full season, a POC allows innovators and stakeholders to test the waters and validate the potential of an idea or technology before investing significant resources into full-scale development.
Further Description:
A Proof of Concept typically involves developing a scaled-down version or prototype of the proposed solution to demonstrate its core functionality, technical feasibility, and potential value proposition. It allows stakeholders to visualize the concept in action, identify technical challenges or limitations, and validate assumptions before proceeding to full-scale development or implementation.
Key Components of a Proof of Concept:
- Problem Definition: Clearly define the problem or opportunity the POC aims to address and the objectives it seeks to achieve.
- Hypothesis Formulation: Develop hypotheses or assumptions about how the proposed solution will address the problem or meet user needs.
- Prototype Development: Build a prototype or demo version of the solution to showcase its key features, functionality, and user experience.
- Testing and Evaluation: Conduct testing and evaluation of the POC in a controlled environment to assess its performance, usability, and scalability.
- Outcome Analysis: Analyze the results and feedback gathered during the POC to determine its success, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions about next steps.
Why is a Proof of Concept Important?
A Proof of Concept serves several important purposes:
- Risk Mitigation: It helps mitigate the risk of investing resources into a concept or technology that may not deliver the expected results.
- Decision Making: It provides stakeholders with tangible evidence and insights to inform decision-making about whether to proceed with full-scale development or investment.
- Innovation Validation: It validates the feasibility and potential of new ideas, technologies, or solutions, fostering innovation and creativity within organizations.
- Stakeholder Alignment: It aligns stakeholders around a shared vision and understanding of the proposed solution, facilitating collaboration and buy-in across teams and departments.
Examples and Usage:
- Developing a prototype of a new mobile app to demonstrate its user interface, features, and functionality to potential investors or customers.
- Testing a new machine learning algorithm on a small dataset to assess its accuracy, performance, and potential for solving a specific problem in data analysis or prediction.
- Building a mockup of a smart device to showcase its integration with existing systems, user interactions, and real-world applications in a controlled environment.
Key Takeaways:
- A Proof of Concept is a demonstration or prototype that validates the feasibility and potential of a new idea, technology, or solution.
- It helps mitigate risks, inform decision-making, foster innovation, and align stakeholders around a shared vision.
- Key components include problem definition, hypothesis formulation, prototype development, testing and evaluation, and outcome analysis.
- By conducting a Proof of Concept, organizations can test ideas, validate assumptions, and make informed decisions about whether to proceed with full-scale development or investment.