Server
What is a Server?
Definition:
A server is a computer or system that is dedicated to managing network resources and providing services to other computers, referred to as clients, within a network. Servers play a crucial role in facilitating communication, data storage, and the execution of various applications across a network. They are designed to handle specific tasks and respond to requests from client devices, ensuring efficient and organized data distribution and processing.
Analogy:
Imagine a server as the central hub of a library, where librarians manage and distribute books to library visitors. In this analogy, the server organizes and provides access to information (like books) for clients, ensuring a seamless flow of data and services within the network.
Further Description:
Servers encompass various types, each serving specific functions within a network:
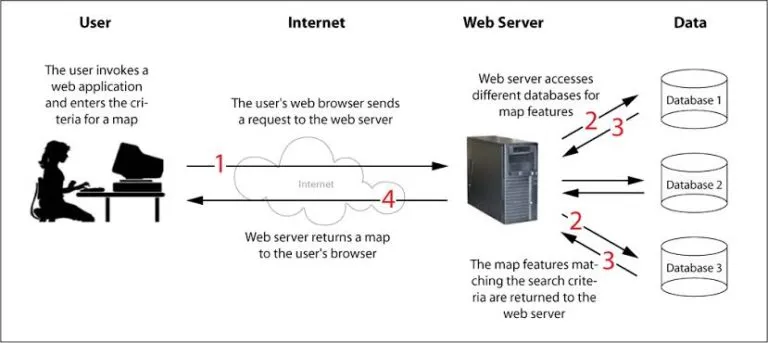
Web Servers: Handle requests from web browsers, delivering web pages and content to users.
File Servers: Manage and store files, allowing users to access and share data within a network.
Database Servers: Store and manage databases, handling data retrieval, storage, and manipulation.
Application Servers: Run and execute applications, processing tasks and requests from clients.
Mail Servers: Manage email communication, handling the sending, receiving, and storage of emails.
Print Servers: Control and manage print jobs, allowing users to print documents over a network.
Why are Servers Important?
Resource Sharing: Servers enable efficient sharing of resources, such as files, applications, and processing power, among connected devices.
Centralized Management: Servers provide a centralized location for data storage, management, and application execution, streamlining network operations.
Data Security: Servers implement security measures to control access, protect sensitive information, and ensure the integrity of data.
Scalability: Scalable server architectures allow for the expansion of resources to accommodate growing demands within a network.
Examples and Usage:
Domain Name System (DNS) Servers: Translate human-readable domain names into IP addresses, facilitating internet communication.
Database Management Systems (DBMS): Utilize servers to manage and retrieve data efficiently, supporting various applications.
Cloud Servers: Offer virtualized computing resources over the internet, providing scalable and flexible solutions.
Key Takeaways:
- A server is a dedicated computer or system that manages network resources and provides services to clients.
- Different types of servers perform specific functions, including web, file, database, application, mail, and print servers.
- Servers play a vital role in resource sharing, centralized management, data security, and scalability within a network.
- Examples of servers include DNS servers, DBMS servers, and cloud servers, each serving unique purposes in network architecture.
Table of Contents