Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)
What is Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP)?
Definition:
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is a communication protocol used for transmitting email messages over the internet. SMTP serves as the standard method for sending emails between servers, allowing users to exchange messages across different email systems and platforms. SMTP defines the rules and conventions for email transmission, including message format, delivery procedures, and error handling mechanisms.
Analogy:
Imagine SMTP as the postal service for the digital world. Just as the postal service facilitates the delivery of physical mail from one location to another, SMTP enables the transfer of electronic messages between email servers. Like postal workers who follow specific procedures for sorting and delivering mail, SMTP servers adhere to predefined protocols to ensure reliable email transmission.
Further Description:
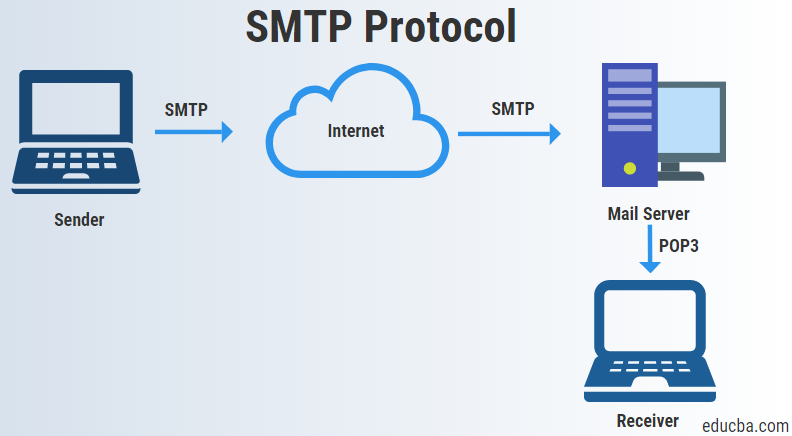
SMTP operates on the client server model, where an email client sends messages to an SMTP server for delivery to the recipient’s server. The recipient’s server then retrieves the incoming message from the sender’s SMTP server and delivers it to the recipient’s email inbox.
Key components of SMTP include:
Message Format: SMTP defines the format for composing email messages, specifying elements such as sender and recipient addresses, subject line, message body, and attachments.
Relaying: SMTP servers relay email messages between sender and recipient servers, ensuring seamless communication across different email domains and networks.
Authentication and Authorization: SMTP supports authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of users and prevent unauthorized access to email servers.
Error Handling: SMTP includes error codes and status messages to indicate delivery status, handling issues such as undeliverable messages, mailbox full errors, and server timeouts.
Why is SMTP Important?
Universal Communication: SMTP enables seamless communication between email users worldwide, regardless of their email service providers or platforms.
Reliability and Scalability: SMTP ensures reliable email delivery, even across large scale networks and diverse infrastructure environments.
Interoperability: SMTP facilitates interoperability between different email systems and applications, allowing users to send and receive messages across various platforms and devices.
Security: SMTP supports encryption protocols such as Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure email transmissions and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
Examples and Usage:
Sending Email: SMTP is used by email clients such as Microsoft Outlook, Gmail, and Apple Mail to send messages to recipients’ email addresses.
Receiving Email: SMTP servers receive incoming messages from other SMTP servers and deliver them to users’ mailboxes for retrieval by email clients.
Automated Email Delivery: Many businesses use SMTP servers to automate email notifications, alerts, and marketing campaigns, ensuring timely communication with customers and stakeholders.
Key Takeaways:
- SMTP is a communication protocol for transmitting email messages over the internet.
- It defines rules and conventions for email transmission, including message format, relaying, authentication, and error handling.
- SMTP enables universal communication, reliability, interoperability, and security in email exchange.
- Examples of SMTP usage include sending and receiving email, automated email delivery, and ensuring secure communication channels.
Table of Contents