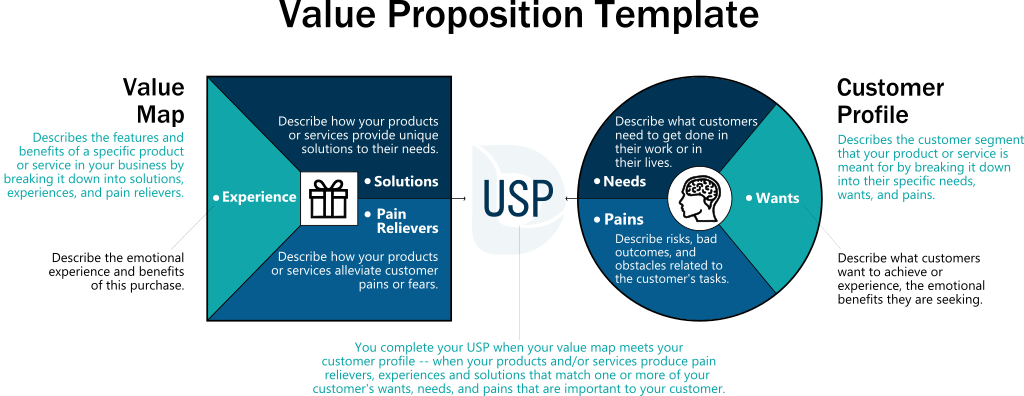
Value Proposition
What is a Value Proposition?
Definition:
In the realm of technology, a Value Proposition refers to the unique set of benefits and advantages that a product or service offers to its users. It articulates why a particular technology solution stands out in meeting the needs and solving the challenges of its target audience. A well-crafted value proposition outlines the specific value that users can expect to gain from adopting a particular technology, emphasizing its superiority over alternative options.
Analogy:
Think of a Value Proposition in technology as a personalized navigation system in a vast tech landscape. Similar to how a navigation system guides you through the quickest and most efficient routes, a technology’s value proposition directs users to the most effective solutions, ensuring their needs are met with precision and efficiency.
Further Description:
The components of a technology Value Proposition include:
Problem Solving: Clearly articulating how the technology addresses specific pain points or challenges faced by users, offering practical solutions and improvements.
Innovation and Uniqueness: Highlighting the distinctive features and innovations that set the technology apart from competitors, showcasing its competitive edge.
User Experience: Emphasizing the positive impact on the overall user experience, illustrating how the technology enhances ease of use, efficiency, and satisfaction.
Performance and Reliability: Communicating the high performance and reliability of the technology, instilling confidence in users about its consistency and dependability.
Cost-effectiveness: Demonstrating the cost-effectiveness of the technology by showcasing how it maximizes value for users while minimizing associated costs.
Why is a Value Proposition Important in Technology?
Decision-Making Aid: Helps potential users make informed decisions by clearly presenting the benefits and advantages of the technology.
Competitive Edge: Establishes a competitive advantage by showcasing what makes the technology superior and more valuable compared to alternatives.
Alignment with User Needs: Ensures that the technology aligns closely with the specific needs and preferences of its target audience.
Long-term Value: Builds trust and loyalty by promising and delivering sustained value throughout the user’s journey with the technology.
Examples and Usage:
Cloud Services Value Proposition: “Our cloud services provide scalable, secure, and cost-effective solutions, allowing businesses to efficiently manage and optimize their digital infrastructure without the need for extensive in-house resources.”
Cybersecurity Solution Value Proposition: “Our advanced cybersecurity solution offers real-time threat detection, rapid response capabilities, and continuous updates to safeguard sensitive data, providing a comprehensive defense against evolving cyber threats.”
AI-powered Analytics Value Proposition: “Harness the power of AI-driven analytics to gain actionable insights, predict trends, and make data-driven decisions, elevating your business intelligence and staying ahead in a dynamic market.”
Key Takeaways:
- A technology Value Proposition is a concise statement that communicates the unique value a technology solution brings to its users.
- It focuses on problem-solving, innovation, user experience, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
- A compelling Value Proposition is crucial for decision-making, establishing a competitive edge, and ensuring long-term user satisfaction and loyalty.
Table of Contents